Translated with the help of AI. We apologize for any errors and would appreciate your help in correcting them.
Poker is a mathematically calculated game. Luck plays a certain role in it, but at a long the long run, the influence of fortune is minimal.
Professionals have a saying in this regard: in one tournament or cash session, the share of luck is 90%, and at the the long run per year – only 10%. 90% of your skill is affected by such a big game.
To play plus, you need to follow a simple rule - to make mathematically positive decisions in each hand. Often, the term "pot odds in poker" is used to determine whether it is possible to call or not pot. We talk about it: what it means, what are the implied odds of the bank, how to calculate them and how to learn how to make +EV decisions in giveaways. Calculating the profitability of a call is a difficult task only at first glance.

1. What are the pot odds in poker?
Poker mathematics seems to be a complex science, difficult to perceive. But you need to master it if you plan to turn poker into a source of income. Let's start the dive with the basic term - bank chances (or pot odds - from the English pot odds). This concept implies the ratio of the current amount of chips in the bank to the rate to be colored pot. It sounds complicated and incomprehensible.
But with a simple example, everything will become clear:
- You opened from the button with a raise of $200, MB fold folded cards in the fold, BB called. The current pot is $450 (two bet bets of $200 and a small blind of $50). On the flop, the villain checks, and you make a small cbet in a third of the sweat – $150.
- His pot chances are: $450 (the amount of chips on the preflop) + $150 (bet on the current street) to $150 - the amount of chips to be delivered. It turns out $600 to $150 or 4 to 1.
2. Poker outs
A 4-to-1 ratio doesn't tell you anything. In a vacuum, it will not tell you whether the call will be profitable or not. For further analysis, you need to get acquainted with the term "outs in poker". You will not be able to collect a ready-made five-card hand in each hand on the flop. Often, your hand will not fall into the flop or turn into a draw - an unprepared combination that has potential chances of strengthening on subsequent streets.
Cards that turn an unmade hand into a strong hand are called outs. The more of them, the stronger your combination is and the more chances he has to win.
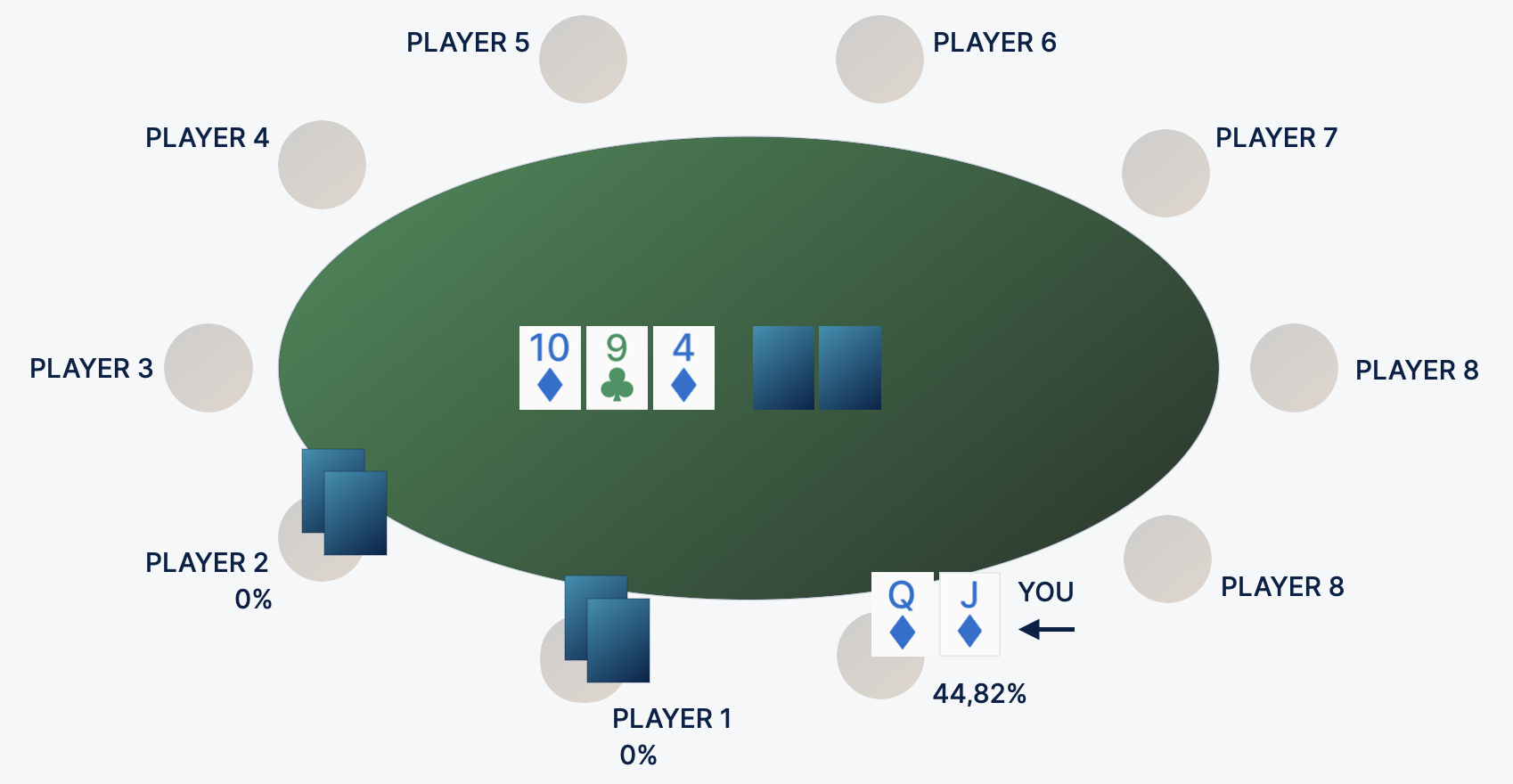
Let's calculate how many outs the jack of diamonds and the Queens will have in the distribution:
- Any diamond card - if a diamond card comes out on the turn or river, it will close the flush (not nuts, but strong enough) - 9 outs.
- King or eight are also good cards that strengthen the hand to the straight. Add another 6 outs, because two cards are counted for the flush.
- Jack or queen - if you are sure that the opponent has hit the nine or ten, the jack or Queens will give you potentially the strongest hand - 6 more outs.
In this distribution, the QJ 21 tambourines have a potential outs for gain. How to translate this number into a chance to assemble a combination?
There are two ways:
- Divide the number of outs by the number of remaining cards in the deck. There are 47 cards left in the deck (52 - 2 yours - 3 total). 21 / 47 = 44.7% get the right card on the turn. The percentage is impressive.
- Add “one” to the outs and multiply by 2. Easier way. (21 + 1) * 2 = 44%. The result with an error turned out to be the same as in the first method.
The article "Probabilities in Poker" provides a method for quickly calculating the chances of strengthening a hand in poker. In it you will also find tables with ready-made calculations for typical situations. With the help of outs, you will calculate the probability of one of the necessary cards falling on subsequent streets. However, odds are not equity. There are such handouts when you catch your outs, but it turns out to be “poisoned”, allowing the opponent to collect nuts - and beat you at the showdown. It is important to learn to think in ranges and analyze each play in an unbiased and emotionless way.
Discounting outs
- Let's go back to the example. Let's think about which of the counted outs can easily be “poisoned”. The obvious answer is hitting a jack or a queen. Both cards close potential streaks, the opponent may have a match with the best kicker, and your pair will be useless against the opponent's set.
We will not subtract the diamond cards from the outs. Potentially, the opponent may have an older flush, but the chance of this is small. A diamond nine or king, which opened on the turn, will give a potential opportunity to increase to a straight flush. After discounting, the number of outs was reduced to 15. The chances of gaining on the turn also became less: (15 + 1) * 2 = 32%. It's still an impressive number.
3. Calculation of pot odds in poker
- We continue to analyze the example with
Suppose a situation when you defended your hand on BB after an open-raise from a button button. The pot is already $450, and on the flop the villain puts another $150. Do you have a chance to make a call? You have already counted the pot of odds – 4 to 1. You need to deliver $150 in the fight for the pot of $600 or 20% (to withdraw the draw to zero, you only need to win one hand out of four).
If you win more often, you play a plus. The bank's chances are compared with the probability of increasing on the flop, if the second value is greater - call profitable.
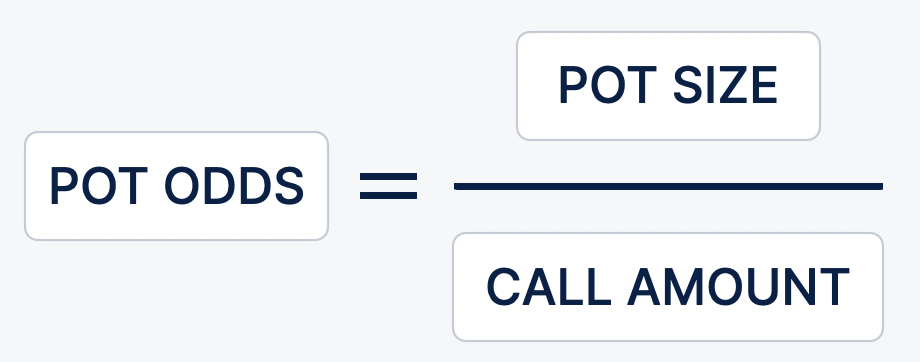
The formula for calculating the pot odds:
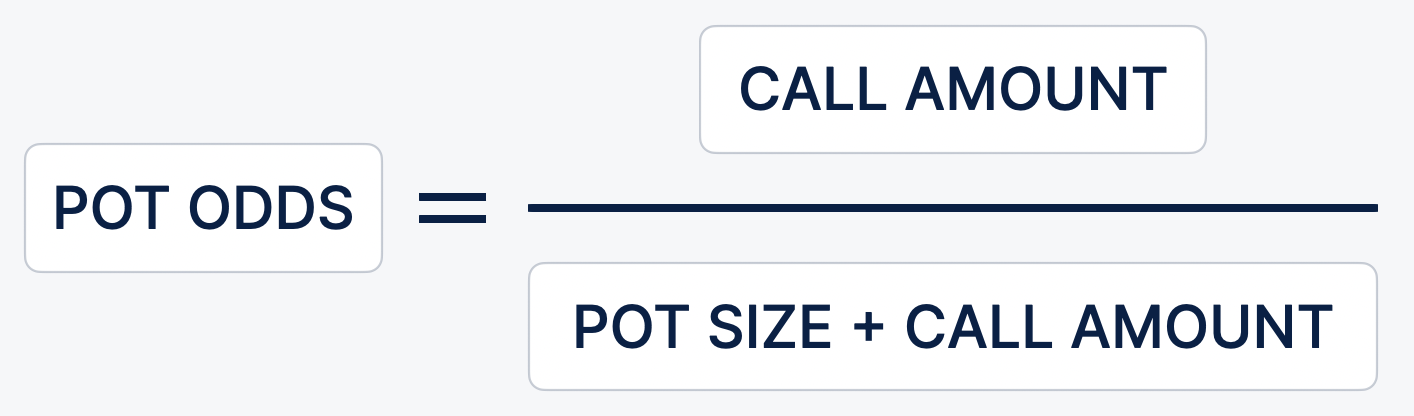
In the example, pot odds is 20%, and the probability of gain taking into account discounted outs is 32%. In this situation, the call on the flop is justified - at a distance it will lead you to a good plus. Another example, but not so unambiguous. You have reached the river with suited connectors 87. Villain puts $500 in a 1000 pot. In terms of chances to call?
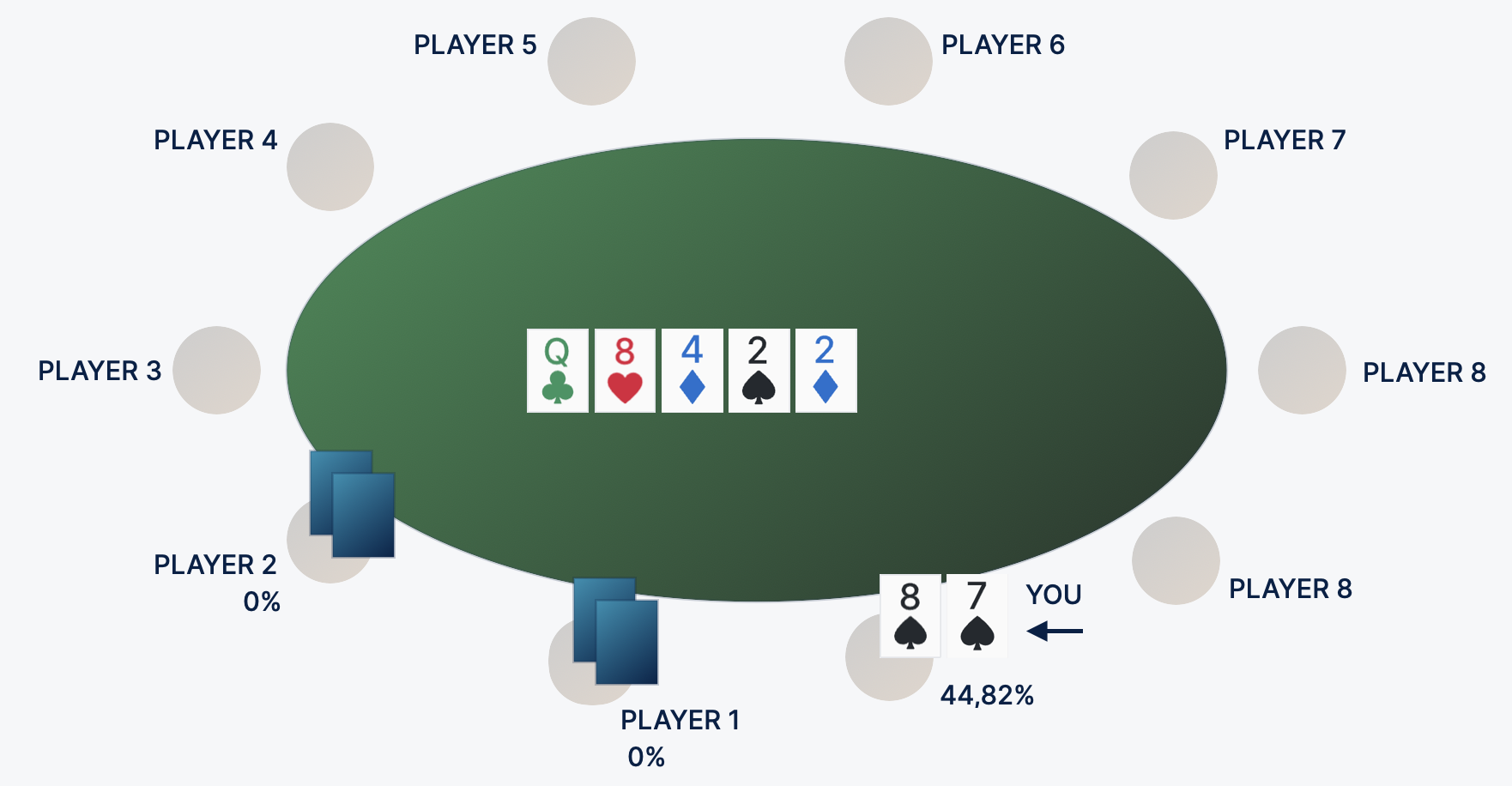
Let's calculate the pot odds:

A pair of eights is far from the strongest combination. This is a bluff-catcher, because with it at the showdown you beat only the “air” in the hands of the opponent. If on the river he made a bet on the value, you are far behind. Pot-odds of 25% offer the following mathematics. If you win the pot in one hand out of four - the call will be zero, more often - you are in the black, less often - you are in the red. If you assume that in this spot the opponent has more than 25% bluff, the call turns out to be profitable. For example, 35%. At the the long run, the call turns out to be positive: 35% equity is higher than the bank's chances by 25% by 10% - this will be a profit at the the long run.
Two calculation formulas
In different manuals, there are two formulas for calculating the pot odds. Poker University talks about both, explaining the difference.
In relative terms.
The calculation according to the formula is simple, but we do not recommend it for beginners, because it is easy to get confused in a relationship and make the wrong decision.
You will get the
final value as a ratio. For example, 3 to 1. Alternative spelling is 3:1.
In percentage terms.
A more familiar way of perceiving information.

In this case, you will get a percentage value that is easier to compare with the chances of gaining on one or two streets.
Pot odds on preflop
It is difficult to correctly calculate the pot odds on preflop, since you do not even know the first three common cards yet. Here it is important to know about the basic chances of strengthening different combinations on the flop. Here are some examples for classic starting combinations: pair and suited connectors.
| Potential Combination on Flop | Start Combination | |||
| Pocket pair | Mast connectors | |||
Probability | Odds | Probability | Odds | |
Two + pair | 11.8% | 7.5 to 1 | 3.49% | 28 to 1 |
Double-sided straight draw | - | - | 9.71% | 9.3 to 1 |
Flush draw | - | - | 10.1% | 8.9 to 1 |
Straight | - | - | 1.31% | 75 to 1 |
Flush | - | - | 0.84% | 118 to 1 |
Chances of the bank when drawing draw pot
You will rarely get a ready hand on the flop (look at the odds in the previous table). And here it is important to learn how to evaluate the strength of the current unfinished combination. We tell you about the classic situations that you will often encounter on post-flop. Chances to strengthen the hand on the river, having a unmade combination on the turn:
Hand on the turn | Probability | Odds |
Gutshot | 8.7% | 10 : 1 |
Double-sided straight draw | 17.4% | 4.7 : 1 |
Flush draw | 19.6% | 4.1 : 1 |
Flush draw with gatshot | 26.1% | 2.8 : 1 |
Flush draw + double-sided straight draw | 32.6% | 2.1 : 1 |
There is a similar table for the probability of amplification from the flop to the turnstile. The data in them will be similar, but the chances of the flop are slightly lower.
4. Table of pot odds in poker for different bet
Playing many tables at the same time, in most hands you make a decision automatically, this skill comes with experience. We share with you another table in which we talk about the minimum equity required for a call of bet of different sizes from an opponent.
| The size of the opponent's bet relative to the value of the pot | Minimum equity required for a call | |
| Percentage | Relative | |
50% | 1/2 | 25% |
67% | 2/3 | 28% |
75% | 3/4 | 30% |
100% (pot-bet) | 1/1 | 33% |
The logic is simple. The smaller the bet size relative to the bank, the less equity is needed for the call. But not everything is so clear. For example, today they are increasingly using an extended bet of a very small size - around 25-35 percent of the sweat. This is enough to knock out completely empty hands. And in the case of a call or a raise and a subsequent loss, you do not lose so many chips.
5. implied odds of the pot
An important part of poker mathematics is the implied odds of the pot. This is not quite an objective indicator that reflects the potential profit from collecting a strong combination.
- Clarifying example - which call on the gatshot will seem more profitable to you if the pot odds in both hands are the same: in effective stacks of 10 big blinds or 150.
- The answer is obvious - the second option is much more interesting. You have an unreadable combination. In the case of collecting it, which happens infrequently, you need to have a chance to win a big pot.
6. How to learn to quickly calculate the pot odds
There are no secrets to quickly calculate the pot odds in poker. Here everything is decided by experience and understanding of formulas with which you are already familiar. The skill is practiced not only during the game in one of the poker rooms, but also during training. We share a secret technique that not all poker players know about - the “rule of two” and the “rule of four”.
- The rule of two - multiply the number of your outs by two - and you will get a chance to strengthen the combination on one street (on the turn OR river).
- The rule of four - multiply the number of outs by four - and get a chance to collect a combination on two streets: from the flop to the river.
7. How to learn to make the right decisions in handouts
Poker is an analytical game. Your decision in the postflop distribution depends on a number of factors. Not only from the cards in hand, but also from the correctness of the logic of reflection.
We share how important it is to build your reasoning:
Opponent's range
Analyze previous actions in the draw, how the opponent behaved, how much the supposed range of his hands has changed, how suitable he is for general cards, etc.
Calculate outs
We recommend that you carefully consider discounting outs. Sometimes it is better to be more pessimistic about the situation than to hope for a map that will be “poisoned”.
Calculate the pot odds
How to do it, you already know.
Estimate the expected win
How many chips you can potentially win and how real it is if you manage to collect the right combination.
Compare the odds
If the probability of gain is higher than the proposed pot of odds, the call will be justified.
This logic seems complicated only at first glance. We recommend you to study the basic video course on poker from Poker University “Fundamentals of preflop and postflop games”. From it you will learn how to play plus tournaments at microlimits. At the same time, you do not have to pay for training, you have the opportunity to get a free poker education through our loyalty program.