Translated with the help of AI. We apologize for any errors and would appreciate your help in correcting them.
To play tournament poker or cash successfully, it is not enough to learn the rules of the game and master how poker combinations are assembled. To achieve victories in the long the run, you will have to work a lot and constantly on the game.
And one of the most important acquired skills is thinking in ranges in poker. We tell in detail what the range in poker is, how the linear range of hands differs from the polar one, how to correctly determine the opponent's range. We also share the working logic of thinking on post-flop.
1. What are poker range
You could hear the phrase from the amateur: “I dropped my top pair on the post-flop, because I put the opponent on the flush”. This is primitive thinking, taking into account only a specific combination, the so-called “card game”. However, when we make a decision on pre-flop or post-flop, it is important to assume that the opponent has the maximum possible starting combinations with which he could demonstrate a particular line in the hand, i.e. lay a range for him.
Range in poker is the whole set of starting hands that your opponent can potentially have in a particular hand. It sounds complicated, but in practice everything is simpler. Let's say you're on a button. Villain makes a raise from an early position in poker. With what combinations is such an action possible? Putting an opponent strictly on pocket aces and kings is a utopia, since there will be much more possible starting combinations in the open-raise range.
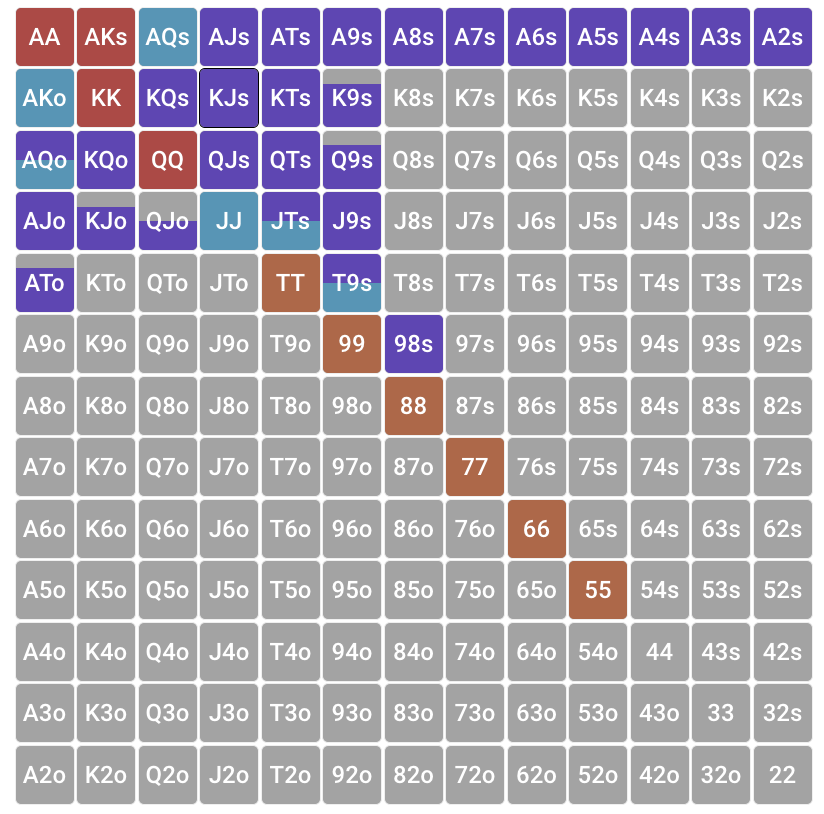
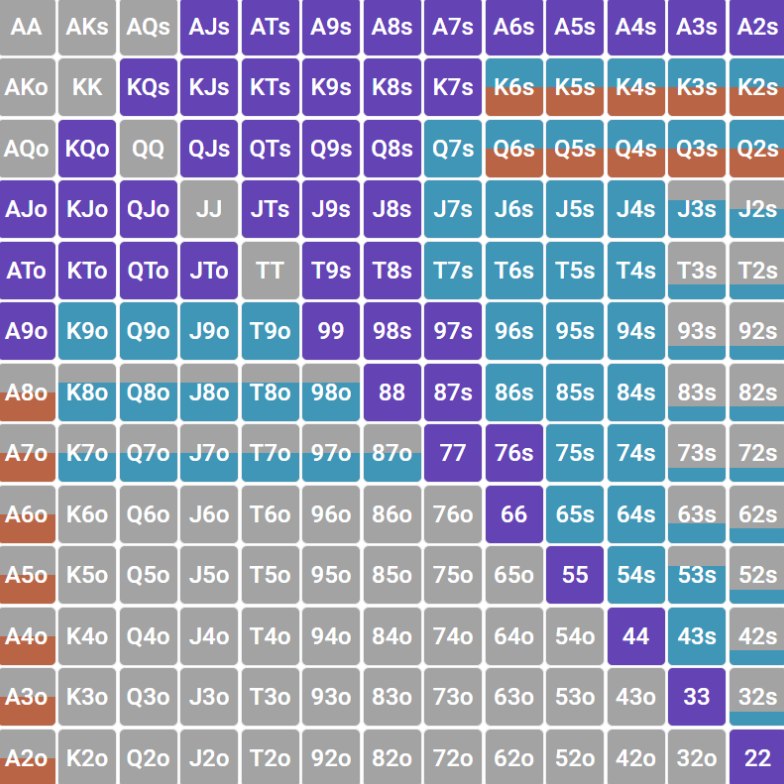
The matrix shows that in addition to aces and kings, with whom you are ready to go up to all-in, from an early position through an bet raise, all pocket pair from sevens and older, suited connectors from 

The easiest way to learn the preflop game range is to use the site's loyalty program and access the video course “preflop and postflop game basics”. It collects and structures key materials for a low-limit profitable poker game.
2. Spectrum notation system
In training materials and forums, it is customary to use a conditional designation system for ranges in poker. Constantly writing “suited connectors older than 98” is long and inconvenient.
Let's introduce you to the designations:
| Symbol | Description |
55-88 | Pocket pair of fives to eights
|
22+ | All pocket pair starting with twos inclusive |
QQ+ | Pocket pair (s)
|
98s+ | Suited connectors 98 and older
|
79s+ | Grade 1 suited connectors (Gap connectors)
|
A2+ | All offsuited aces
|
Broadway |
3. Range Thinking in Poker
For successful range thinking, it is important to figure out how many combinations are possible in each starting hand. Before reading further, try to answer the question - how many options for making a pocket pair of aces are there in Texas Hold 'em?
Correct Answer:
- Six.
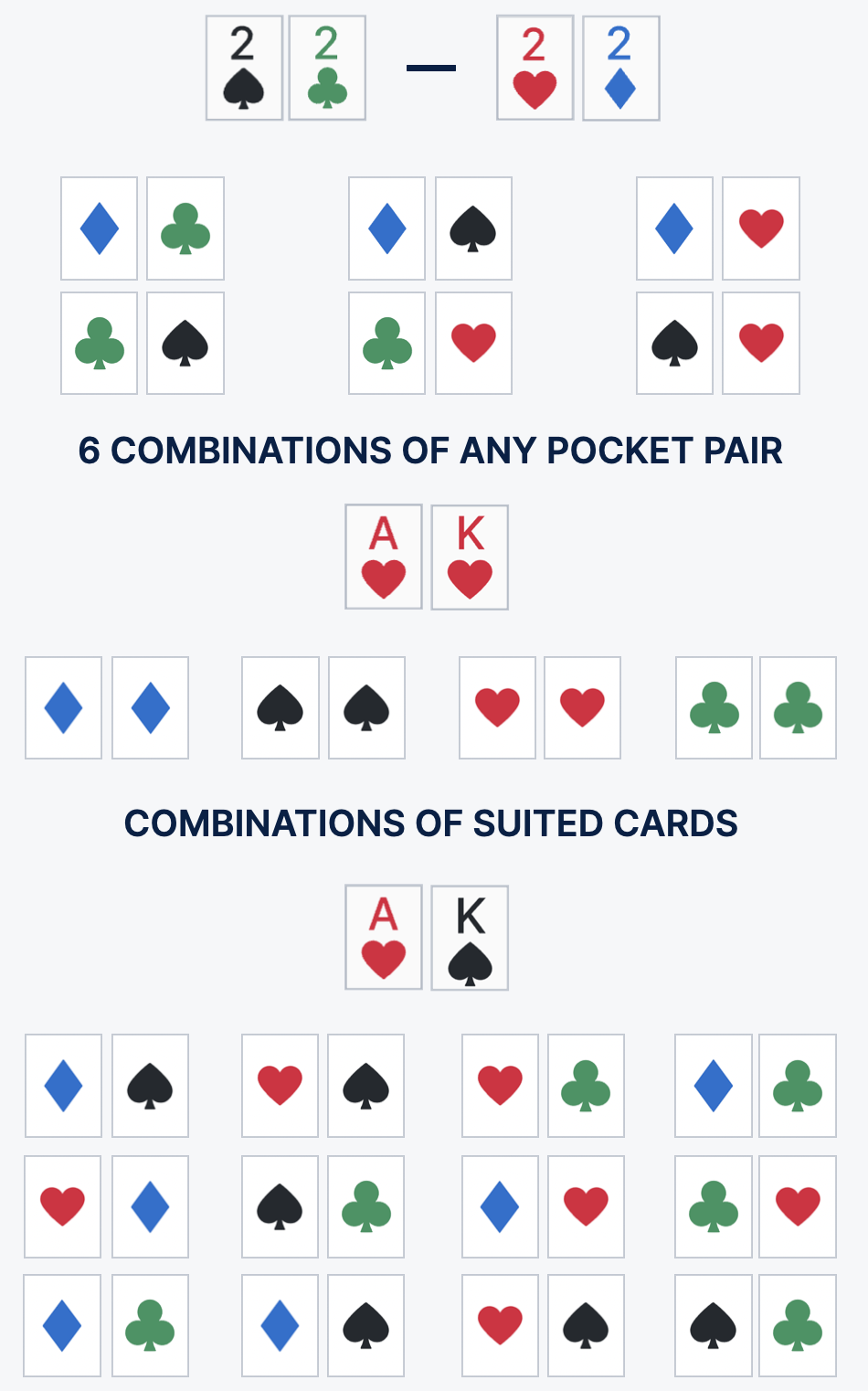
You will not need these numbers when deciding on a collegue in a difficult hand, but knowing the internal mathematical structure of the game forms a subconscious understanding of strategic concepts. The theory is also important.
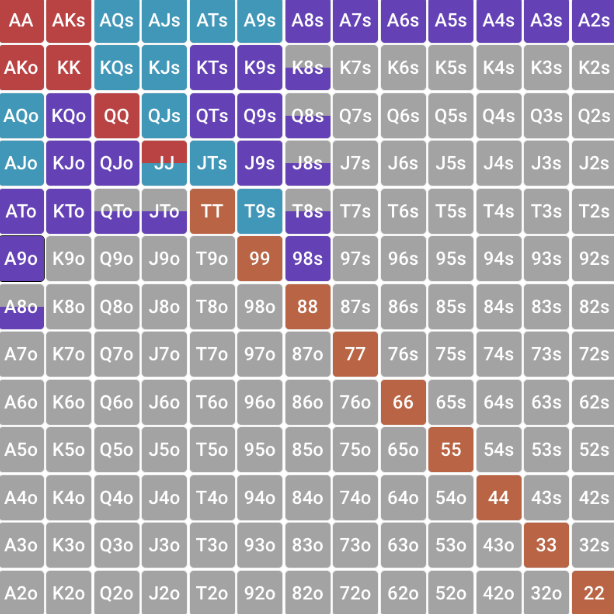
Linear range
Linear is a range containing strong, medium and (possibly) weak hands. An important condition is that these hands do not have a scatter on the card matrix.
- Example: opening range from middle position.
Polar range
Range differs from linear by the presence of "poles": separated groups of cards, both strong and weak. The polar range contains practically no "middle", i.e. medium strength maps.
- Example: drange of 3bet from the big blind (BB) against the style from the late positions. All cards of medium strength are played through call (very weak ones go into fold).
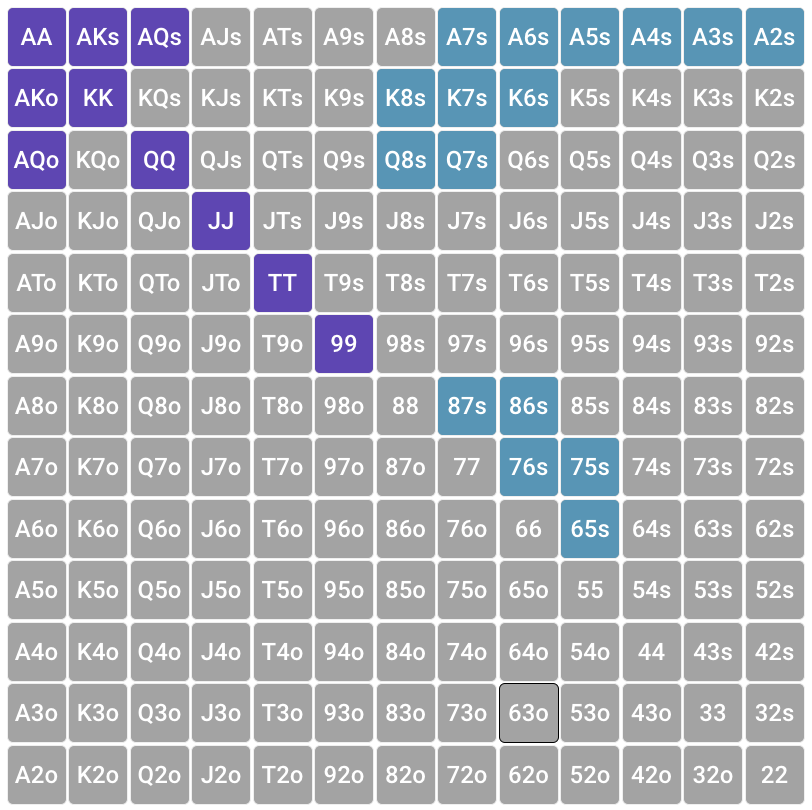
Capped range
Assessing the range of our opponent, we (along with linearity and polarity) must consider another important parameter: is the range of interest limited, does it have a limit? The range, which for some reason is limited, has limits (that is, it cannot contain certain groups of hands), is called trapped.
Capped bottom range
In the example in paragraph 1 (“Opening range from an early position”), we see an example of a range that is not only linear, but also limited (capted) from the bottom, i.e. does not have frankly weak hands located at the bottom of the game matrix. Since from an early position we tend to open mostly strong hands, we can assume that weak hands will be less likely to occur in this range.
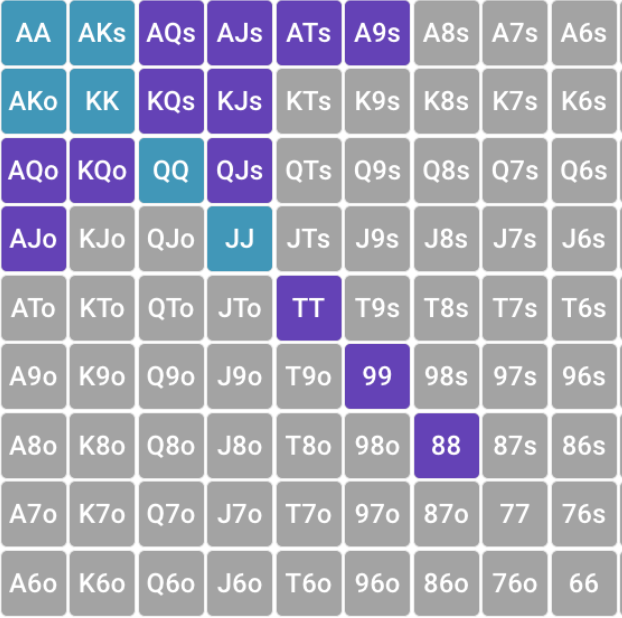
Capped capped range
Also, the range can be trapped (limited) not only from the bottom, but also from the top. This, for example, will be the cold-call range on the preflop, because we assume that all strong hands (“top”) will be played on the preflop through 3-bet.
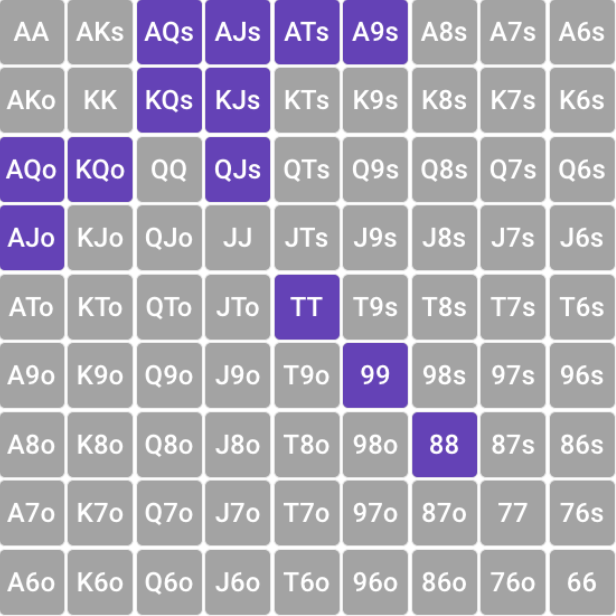
Range, dipped on the vellya capped
On postflop, the range can drip not only in terms of fullness, but also in terms of strength (vellya). Since with a strong hand, players usually tend to place bet (raises and betas), then passive play through a check in most cases means that their range is weak, that is, cap (limited) on the vellya. Therefore, the situation when, for example, the preflop aggressor refuses to continue betting on the flop (and especially does it twice both on the flop and on the turn!) is a sure sign of the value of its range on the velly and a good reason to intercept the initiative to take the pot with the help of bluff.
4. How not to read hands
Consider this on a specific hand:
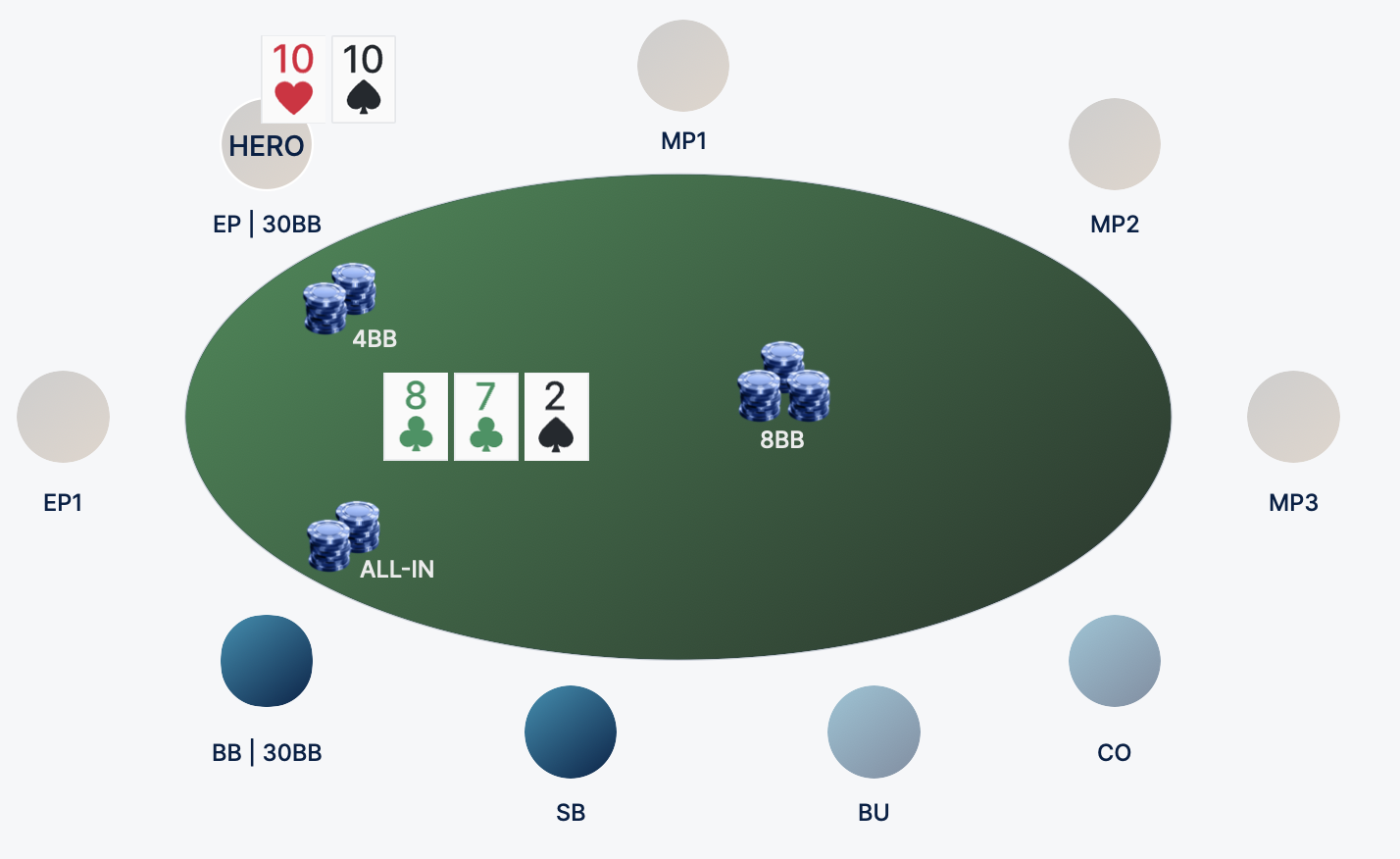
Here are a few arguments that often occur in the mind of beginners, but are erroneous in nature:
- Opponent plays in a secret style
He probably has a set against which we have a bit of equity. - Villain loose
At best, he has a flush draw - you need to call.
- Opponent resembles a fish
Most likely, he has a top pair - you need to equalize. - Villain - maniak
In such a situation, he can have any two random cards - the call is justified.
At first glance, such thoughts seem logical, but you should know your opponent perfectly well, which is rare in tournaments. It is important to put the entire range of starting combinations on the preflop to the opponent to determine the action in a particular hand.
Thus, understanding all the options for starting hands that the opponent may have in this bank, you can assume all the options for hitting the opponent:
- Number of top pairs;
- Number of dopers;
- Sets;
- Quantity of draw (flush draw and straight draw).
And so on. It is important for a poker player to learn how to think not in narrow categories and not guess, but how to set a voluminous range of opponent's hand options and correctly narrow the range by analyzing each of his action.
5. How to read your hands correctly using range thinking
You already know how not to reason in the distribution. Let's now consider the correct logic of thinking in ranges. Hold 'em has only 1,326 starting combinations. Having two pocket cards with known values reduces the potential number of opponent's hands to 1,225.
Up to the moment when the player has performed an action on the preflop - he can have any of these combinations. However, after a specific decision, the number of starters is reduced.
In the example above, the villain played through a call. Let's assume that he is a player acting on about the average range of BB protection, which is presented above, or has even a slightly narrower range. In this case, you can set him several options for getting into the board, with which the villain can go to all-in on the flop.
We begin to discuss specific combinations and our probability of winning against them:
| Potential opponent's hand | Number of combinations | Equity TT in case of call |
Set
| 9 | 12% |
Two pair
| 9 | 29% |
Overpair | 6 | 88% |
Flush draw | 44 | 52% |
Straight draw
| 16 | 65% |
Top pair
| 75 | 79% |
After analyzing the range of possible opponent's hands, we see that in most cases we will have an edge in terms of equity (probability to win) and therefore we can confidently call. In poker, this is called a plus decision on the the long run. Specifically, in this case, we can see the opponent's 87 (two pair) and be behind in the strength of the hand. But at the the long run, having played a similar pot 100 times, we will be in the black on chips.
Flop Texture Evaluation and Range Thinking
If we continue to analyze the game thinking by the example of this situation, we can also judge who and how the board is more suitable (issued cards) in order to understand the strategic opportunities in this pot. Flop 8-7-2 definitely suited the opponent on BB. He has more different small cards that got into this board structure. Of your starters, only over pairs, flush draw, top pairs, straight draw and sets will be hooked for such a flop. At the same time, variants of possible hits in descending order of their number are listed here.
It is important to voice in your thoughts the options for hitting not chaotically, but in descending order. So that the mind understands what is more and what is less. Usually, it is enough to set the top 3 options to understand 80% of the opponent's range. This is enough to make a good strategic decision.
6. How to learn to think in ranges
Of course, the skill of thinking in ranges is not formed immediately.
It is best to include in your self-education program a regular viewing of Exan13 tournament debriefs, paying close attention to the thoughts of an experienced player about handings and decision-making in them. Alexey Exan13 gives very detailed explanations that are understandable to novice players. It is also very useful to independently disassemble range in programs like Flopzilla, to look at the equity of different hands against each other, as well as the equity of certain hands against the range, and so on. Now there are various simulators for calling-station phones on this topic.







 |
| 
 |
| 
 |
|  |
| 



 |
| 
 |
| 

 |
| 

 |
|